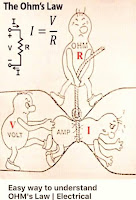
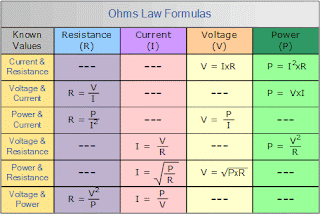
Ohm's Law:
Ohm's law states that the current through the conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points.


where,
I is Current flowing measured in Ampere.
V is Voltage measured in volts.
R is resistance measured in Ohm.
Ohm's law is an emperical law, a generalization from many experiments that have shown that current is approximately proportional to electric field for most materials. It is less fundamental than Maxwell's equation and is not always obeyed.
In physics, the term Ohm's law is also used to refer to various generalization of the law, for example the vector form of the law used in electromagnetic and materials science.

where,
J isCurrent density
E is electric field
σ (sigma) is conductivity









No comments:
Post a Comment